傻大方提要:【绝!真就一文全懂!Netty线程模型+启动详细分析+内存管理( 五 )】private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {try {// 确保 Channel 处于 openif (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {return;}boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;// 真正的...
按关键词阅读:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {try {// 确保 Channel 处于 openif (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {return;}boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;// 真正的注册动作doRegister();neverRegistered = false;registered = true;pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();safeSetSuccess(promise);//设置注册结果为成功pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();if (isActive()) {//如果是首次注册,发起 pipeline 的 fireChannelActiveif (firstRegistration) {pipeline.fireChannelActive();} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {beginRead();}}} catch (Throwable t) {closeForcibly();closeFuture.setClosed();safeSetFailure(promise, t);}}如果 Channel 处于 open 状态 , 则调用 doRegister() 方法完成注册 , 然后将注册结果设置为成功 。 最后判断如果是首次注册且处于激活状态 , 则发起 pipeline 的 fireChannelActive() 。
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {boolean selected = false;for (;;) {try {// 注册到NIOEventLoop的Selector上selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().selector, 0, this);return;} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {if (!selected) {eventLoop().selectNow();selected = true;} else {throw e;}}}}因为当前没有将一个ServerSocket绑定到一个address
if (isActive()) {//如果是首次注册,发起 pipeline 的 fireChannelActiveif (firstRegistration) {pipeline.fireChannelActive();} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {beginRead();} } public boolean isActive() {return this.javaChannel().socket().isBound();} protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;if (selectionKey.isValid()) {this.readPending = true;int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();if ((interestOps}}}这里将selectionKey的监听操作设置为之前构造NioServerSocketChannel设置的SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
doBind0()追溯doBind0()的实现 , 我们可以发现会调用初始化时NioMessageUnsafe的bind方法
@Overridepublic final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {// ...boolean wasActive = isActive();// ...doBind(localAddress);if (!wasActive}});}safeSetSuccess(promise);}doBind(localAddress) 调用JDK的代码 , 实现了端口绑定
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {//noinspection Since15javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());} else {javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());}}绑定后isActice()返回true , fireChannelActive() 被调用 。
内存管理ByteBuffer、ByteBuf为了减少频繁I/O操作 , 引进了Buffer的概念 , 把突发的大数量较小规模的 I/O 整理成平稳的小数量较大规模的 I/O。 Java NIO封装了ByteBuffer组件 。 ByteBuffer具有4个重要的属性:mark、position、limit、capacity, 以及两个重要的方法clear()、flip()
- position:读写指针 , 代表当前读或写操作的位置 , 这个值总是小于等于limit的 。
- mark:在使用ByteBuffer的过程中 , 如果想要记住当前的position , 则会将当前的position值给mark , 需要恢复的时候 , 再将mark的值给position 。
- capacity:代表这块内存区域的大小 。
- limit:初始的Buffer中 , limit和capacity的值是相等的 , 通常在clear操作和flip操作的时候会对这个值进行操作 , 在clear操作的时候会将这个值和capacity的值设置为相等 , 当flip的时候会将当前的position的值给limit , 我们可以总结在写的时候 , limit的值代表最大的可写位置 , 在读的时候 , limit的值代表最大的可读位置 。
public final Buffer clear() {position = 0; //设置当前下标为0 limit = capacity; //设置写越界位置与和Buffer容量相同 mark = -1; //取消标记 return this; } 在读操作之前调用flip()public final Buffer flip() {limit = position;position = 0;mark = -1;return this; ByteBuffer具有以下缺陷- ByteBuffer长度固定 , 一旦分配完成 , 它的容量不能动态扩展和收缩 , 当需要编码的POJO对象大于ByteBuffer的容量时 , 会发生索引越界异常;
- ByteBuffer只有一个标识位控的指针position , 读写的时候需要手工调用 flip() 和 clear() 等;
- ByteBuffer的API功能有限 , 一些高级和实用的特性它不支持 , 需要使用者自己编程实现 。
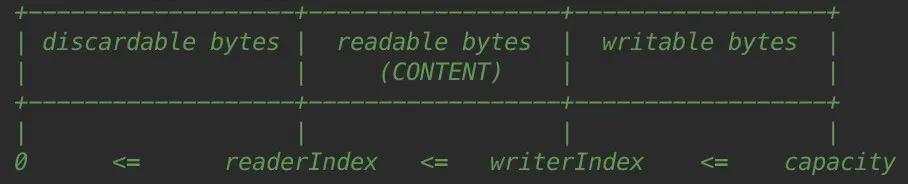 文章插图
文章插图
稿源:(未知)
【傻大方】网址:http://www.shadafang.com/c/111J293N2020.html
标题:绝!真就一文全懂!Netty线程模型+启动详细分析+内存管理( 五 )