按关键词阅读:
 文章插图
文章插图
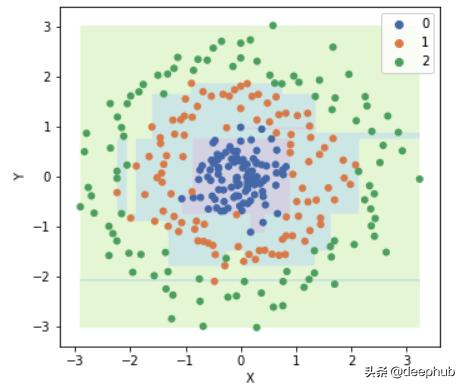
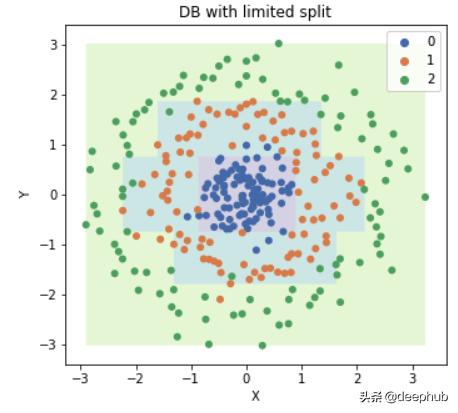
如何应对过度拟合?从上一节中 , 我们知道决策树过拟合的幕后原因 。为了防止过度拟合 , 我们需要在某个时候停止拆分树 。因此 , 我们需要引入两个用于训练的超参数 。它们是:树的最大深度和叶子的最小尺寸 。让我们重写树的构建部分 。
def decision_tree(X, y, max_dep = 5, min_size = 10):# train the decision tree model with a datasetcorrect_prediction = 0def build_tree(X, y, dep, max_dep = max_dep, min_size = min_size):# recursively build the treesplit = get_split(X, y)if split['gain'] == 0 or dep >= max_dep or y.shape[0] <= min_size:nonlocal correct_predictionleaf = Leaf(y)correct_prediction += leaf.counts[leaf.prediction]return leafleft, right = test_split(split['index'], split['value'], X, y)left_node = build_tree(left['X'], left['y'], dep + 1)right_node = build_tree(right['X'], right['y'], dep + 1)return Decision_Node(split['index'], split['value'], left_node, right_node)root = build_tree(X, y, 0)return correct_prediction/y.shape[0], root现在我们可以重新训练数据并绘制决策边界 。
 文章插图
文章插图
树的可视化接下来 , 我们将通过打印出决策树的节点来可视化决策树 。节点的压痕与其深度成正比 。
【Python手写决策树并应对过度拟合问题】def print_tree(node, indent = "|---"):# print the treeif isinstance(node, Leaf):print(indent + 'Class:', node.prediction)returnprint(indent + 'feature_' + str(node.index) +' <= ' + str(round(node.value, 2)))print_tree(node.left, '|' + indent)print(indent + 'feature_' + str(node.index) +' > ' + str(round(node.value, 2)))print_tree(node.right, '|' + indent)结果如下:
|---feature_1 <= 1.87||---feature_1 <= -0.74|||---feature_1 <= -1.79||||---feature_1 <= -2.1|||||---Class: 2||||---feature_1 > -2.1|||||---Class: 2|||---feature_1 > -1.79||||---feature_0 <= 1.62|||||---feature_0 <= -1.31||||||---Class: 2|||||---feature_0 > -1.31||||||---feature_1 <= -1.49|||||||---Class: 1||||||---feature_1 > -1.49|||||||---Class: 1||||---feature_0 > 1.62|||||---Class: 2||---feature_1 > -0.74|||---feature_1 <= 0.76||||---feature_0 <= 0.89|||||---feature_0 <= -0.86||||||---feature_0 <= -2.24|||||||---Class: 2||||||---feature_0 > -2.24|||||||---Class: 1|||||---feature_0 > -0.86||||||---Class: 0||||---feature_0 > 0.89|||||---feature_0 <= 2.13||||||---Class: 1|||||---feature_0 > 2.13||||||---Class: 2|||---feature_1 > 0.76||||---feature_0 <= -1.6|||||---Class: 2||||---feature_0 > -1.6|||||---feature_0 <= 1.35||||||---feature_1 <= 1.66|||||||---Class: 1||||||---feature_1 > 1.66|||||||---Class: 1|||||---feature_0 > 1.35||||||---Class: 2|---feature_1 > 1.87||---Class: 2总结与其他回归模型不同 , 决策树不使用正则化来对抗过度拟合 。相反 , 它使用树修剪 。选择正确的超参数(树的深度和叶子的大小)还需要进行实验 , 例如 使用超参数矩阵进行交叉验证 。
对于完整的工作流 , 包括数据生成和绘图决策边界 , 完整的代码在这里:github/JunWorks/ML-Algorithm-with-Python/blob/master/decisiontree/decisiontree.ipynb
作者:Jun M
deephub翻译组

稿源:(未知)
【傻大方】网址:http://www.shadafang.com/c/111T314032020.html
标题:Python手写决策树并应对过度拟合问题( 二 )